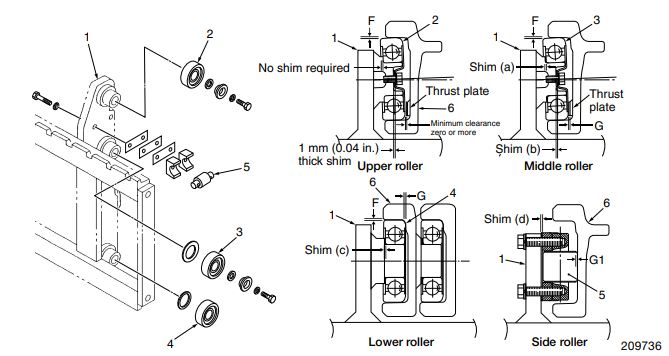
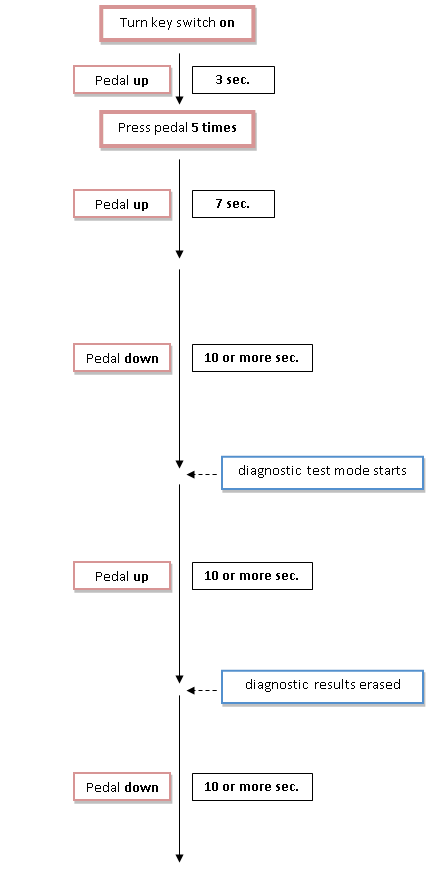
Cómo borrar los códigos de error de carretillas elevadoras Caterpillar y Mitsubishi

P: ¿Cómo borro los códigos de error de una carretilla elevadora Caterpillar / Mitsubishi? R: Borrar los códigos de montacargas Caterpillar y Mitsubishi es un proceso que requiere mucha precisión. Es útil estar familiarizado con éstos pasos antes de intentar borrar los códigos de error. También se recomienda que utilice un cronómetro para controlar el […]
Read Post