The term forklift truck is a fairly broad term that can be used for a number of different vehicles. When people think of forklifts, they usually imagine the small vehicle with two forks on the front that’s used for lifting pallets. However, forklift trucks come in a number of different sizes and models.
With so many forklift types to choose from it can be difficult to find the forklift perfect for your environment. Choosing the wrong forklift can waste time, money, and effort.
Let’s take a look at some of the most popular forklift classifications.
Class I: Electric Motor Rider Trucks
The following are examples of Class I powered industrial trucks.
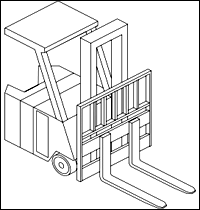
Lift Code 1: Counterbalanced Rider Type, Stand Up.
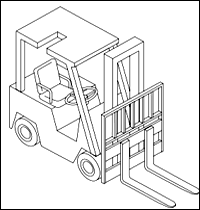
Lift Code 6: Counterbalanced Rider, Pneumatic or Either Type Tire, Sit Down.
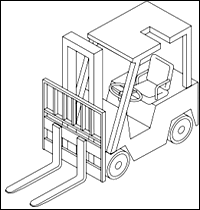
Lift Code 5: Counterbalanced Rider, Cushion Tires, Sit Down.
Counterbalance Forklift Truck
This is the proper name of the traditional forklift that everyone is familiar with. It’s called a counterbalance forklift because the load that’s being carried in the front is counterbalanced by a heavy weight mounted on the back of the vehicle. The forks are often attached to a mast that can raise the load several feet up off the ground. This makes it easier to move the load, plus some masts are high enough that the load can be placed on the second level of a shelving system.
Counterbalance forklift trucks can be powered by gas, diesel, or electric batteries. They are often used in warehouses, construction sites, and other shipping/storage facilities.
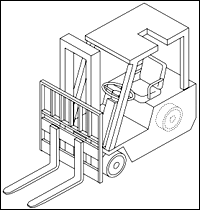
Lift Code 4: Three Wheel Electric Trucks, Sit Down.
The Three-Wheel Counterbalance Forklift
This type of forklift is very similar to the standard counterbalance forklift with one exception: it features a third wheel located in the middle of the back part of the forklift. This gives the vehicle much more maneuverability. While standard counterbalance forklifts need a good amount of space to make turns, a three-wheel forklift can actually spin in a very tight circle.
Three-wheeled counterbalance forklifts are mainly used in warehouses and loading docks where there isn’t much room for maneuvering or turning.
Class II: Electric Motor Narrow Aisle Trucks
The following are examples of Class II powered industrial trucks.

Lift Code 1: High Lift Straddle.

Lift Code 2: Order Picker.

Lift Code 3: Reach Type Outrigger.
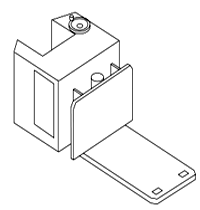
Lift Code 6: Low Lift Platform.

Lift Code 6: Low Lift Pallet.
Powered Hand Truck
This is basically the same as a hand pallet truck except it includes a small electric motor. This motor does the work of lifting the load and moving the hand truck. The operator guides it, but doesn’t have to actually push the load.

Lift Code 4: Side Loaders: Platforms.

Lift Code 4: Side Loaders: High Lift Pallet.
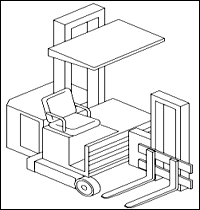
Lift Code 4: Turret Trucks.
Specialty Trucks
These are just the most common types of forklift trucks. There are some specialty trucks that are used in specific industries or in certain settings, such as a sideloader that picks up and carries pallets to the side of the vehicle instead of in the front. Teletrucks, a new type of forklift, have an extending mast that is connected to a boom instead of a straight mast, giving them a wider range of motion.
Class III: Electric Motor Hand Trucks or Hand/Rider Trucks
The following are examples of Class III powered industrial trucks.

Lift Code 1: Low Lift Platform.

Lift Code 2: Low Lift Walkie Pallet.

Lift Code 3: Tractors

Lift Code 4: Low Lift Walkie/Center Control.

Lift Code 5: Reach Type Outrigger.

Lift Code 6: High Lift Straddle.

Lift Code 6: Single Face Pallet.
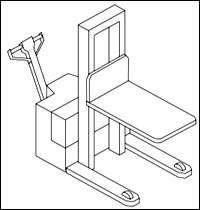
Lift Code 6: High Lift Platform.

Lift Code 7: High Lift Counterbalanced.
Reach Trucks
A reach truck looks like a very small type of counterbalance forklift. However, it doesn’t have any type of counterbalance weight on it. Instead, it uses a pair of stabilizing legs to keep from tipping over. Reach trucks aren’t meant for moving loads long distances. Instead, this type of forklift has a special fork carriage that can be extended out from the vehicle. This allows the reach truck to place pallets of products into shelving. It can lift things upwards of ten meters or more. Some reach trucks have a cab that tilts so that the operator can have a better view of the fork carriage, while others actually have small cameras attached to the carriage. Reach trucks are used in large warehouses that store pallets several rows high on shelving or have deep shelves that can hold multiple pallets. The ability to reach into shelving or reach up higher than counterbalance forklifts makes them invaluable in these settings. However, reach trucks are not really designed for outdoor use. They don’t do well on uneven surfaces or rough terrain.

Lift Code 8: Low Lift Walkie/Rider Pallet and End Control.
Class IV: Internal Combustion Engine Trucks (Solid/Cushion Tires)
The following are examples of Class IV powered industrial trucks.

Lift Code 3: Fork, Counterbalanced (Cushion Tire).
Class IV forklifts are rider fork trucks, with cabs and seated controls, internal combustion engines, and solid or “cushion” tires. They are usually counterbalanced.
Class V: Internal Combustion Engine Trucks (Pneumatic Tires)
The following are examples of Class V powered industrial trucks.

Lift Code 4: Fork, Counterbalanced (Pneumatic Tire).
Class V forklifts are rider fork trucks, with cabs and seated controls, internal combustion engines, and pneumatic tires. They are typically counterbalanced.
Class VI: Electric and Internal Combustion Engine Tractors
The following are examples of Class VI powered industrial trucks.

Lift Code 1: Sit-Down Rider (Draw Bar Pull Over 999 lbs.).
Class VI forklifts are sit-down rider, tow tractor lifts. They are supplied with electric or internal combustion engines.
Class VII: Rough Terrain Forklift Trucks
Class VII – Rough terrain forklift is a generic term used to describe forklifts typically intended for use on unimproved natural terrain and disturbed terrain construction sites. However, the term “rough terrain” does not imply that the forklift can be safely operated on every conceivable type of terrain. Rough terrain forklifts have inflatable tires with thicker treads which allows it to gain stability on uneven surfaces. It also has high maneuverability and a powerful engine that allows it to reach higher speeds. Essentially, rough terrain forklifts are built to be durable. This makes them the ideal vehicles for transporting heavy loads across long stretches of rough terrain, with some models being capable of handling 3 tons at a time. Rough terrain forklifts have counterbalances at the back of the truck that are calibrated carefully to avoid overbalancing issues. These trucks are capable of operating in the snow, mud, and ice with no problems.
There are three basic types of rough terrain forklift:
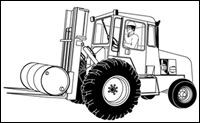
Vertical mast type.
This is an example of a ruggedly constructed forklift and is designed to be used primarily outdoors.

Variable reach type.
This is an example of a vehicle equipped with a telescoping boom, which enables it to pick and place loads at various distances and lift heights in front of the machine. The ability to reach out in front of the forklift allows the operator flexibility in the placement of a load.

Truck/trailer mounted.
This is an example of a portable self-propelled rough terrain forklift that is typically transported to the job site. It is mounted on a carrier to the back of a truck/trailer and is used to unload heavy items from the truck/trailer at the job site. Note that not all truck/trailer mounted forklifts are rough terrain forklifts.
